- About the Department
- Faculty Profile
- Courses offered
- PO and CO
- Certificate / Add-on courses
- Teaching-learning
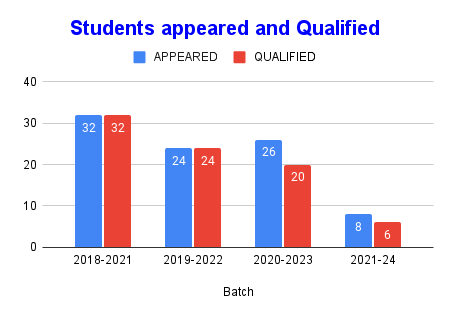
- Result and student progression
- Departmental Activities and Achievements
- MOU with other Institution
- Alumni
- Photo Gallery

Mathematics is the most beautiful and most powerful creation of the human spirit.
— Stefan Banach, Polish mathematician
Vision
Our vision is that our young learners, guided by us, follow a path to enrichment, both spiritual and temporal, for themselves, their families and the society.
Mission
Our institution is situated at the southern fringe of Kolkata. This encourages students from rural and semi-urban areas to enroll at our college in a significant number. Some of them are from economically disadvantaged backgrounds and some are first generation college-goers. Our mission is to inculcate a sense of mathematical derivation based on mathematical logic and usage of modern tools like computer programming to develop ability to solve problems, both theoretical and practical, so they can face the world after college.
Brief History of the Department
The Department of Mathematics of Sammilani Mahavidyalaya started in 1997. At first, only the general course for mathematics was started. The Honours course started in 2007. At present, the department has about 100 Honours and 200 general students registered under the University of Calcutta under the CBCS system, 2018 and CCF system, 2020. There are four Govt. approved faculty members in the department. In addition to the Honours and general courses, the Mathematics faculty members used to take extra classes in the departments of Commerce, Computer science and Chemistry classes as and when required.
Infrastructure
The department uses regularly, a well-equipped Mathematics software laboratory with about 20 computers for practical purposes of the departmental students and two smart classrooms other than regular allotted classrooms in the college. The department also maintains a departmental library( which are nothing but the collections of complimentary copies of books given by the publishers to the departmental teachers) with about 500 books for the benefit of students as well as teachers, with proper accession and Book issue register maintained by the department.
Teaching and communication
Faculty members are committed to take regular classes for completion of syllabus within the stipulated period mentioned by the parent university. Tutorial and extra classes (in both online and offline mode) are taken for the benefit of the students. Orientation program and Entry level assessment test are usually taken for new cummer 1st semester students in each session. Class tests are taken frequently after completion of respective topics in the syllabus. Internal examination and Tutorial examinations( i.e., formation of projects in each Honours course followed by presentation and viva-voce) are the internal college components of Calcutta University Examination. Teaching by the student’s seminar method is also applied for better learning of each student.
Apart from that, teachers of the department regularly communicate with the students for mentoring and address their needs or problems in the classroom and beyond. Faculties also guide the students for their future progression in the academic field as well as job market. Whatsapp groups were formed during the lockdown period and maintained till now for different semester students and also for overall all students of the department(both current and Alumni) for better communication.
Alumni
The alumni of the department maintain their connection with the department by contacts in whatsapp groups and help the department and current students as and when required. They participate in all departmental programs.
Activity of the Department
The department regularly organizes academic programs like Seminars, Webinars, Special Lecture Series by eminent speakers, lectures by alumni members, educational tours for all departmental students etc. Add-on courses conducted by the faculties, mini research projects by the students guided by the faculty members are part of departmental activities. The department jointly arranges programs like celebration of Mathematics Day with K.K.Das college, which involves inter-college quiz competition, poster presentation, wall magazine etc. Students whole-heartedly participate in college or district sports securing positions in individual events. In spite of these, students used to take active part in different co-curricular activities of the college.
Collaboration
Sammilani Mahavidyalaya has an active collaboration agreement (MOU) with K. K. Das College, Garia,a neighboring college, since 2020, under which faculty members of Department of Mathematics of both the colleges teach students of department of mathematics of the two colleges under a combined routine made by the teachers of mathematics department of both the colleges as per the resolution taken in the common meeting held before the commencement of each session, thus augmenting the faculty resources. Under MOU different programs like Seminars, Lecture series by eminent external speakers, Celebration of Mathematics Day etc. are regularly arranged jointly by the department of mathematics of both the colleges. This collaboration was particularly useful during the covid lockdown period when students of Sammilani Mahavidyalaya and K.K.Das College were taught through online classes taken by the faculty members of both the colleges.
Academic Audit
Here is the link to view Academic Audit of the department of Mathematics for 2022-23 and 2021-22.
SWOC Analysis
Strength-Weakness-Opportunity-Challenges that is SWOC analysis is essential for the overall improvement of any department. Here is the link to the detail : SWOC.

Dr. Sumita Das
Designation: Associate Professor
Email: das.susmita752@gmail.com
Phone Number: 9433097254Get Detail »

Dr. Malay Roy
Designation: Assistant Professor
Email: malaydear@gmail.com
Phone Number: 9830509029Get Detail »

Smt. Sukti Sen
Designation: SACT
Email: sensukti819@gmail.com
Phone Number: 9903859310Get Detail »

Dr. Raju Haldar
Designation: SACT
Email: r_haldar@yahoo.com
Phone Number: 7595880408Get Detail »
1. The CCF-2022 System (Academic Session 2023-24 onwards):
(a) Four-Year (8 Semester) Honours and Honours with research courses with Mathematics Major
and
(b) Three-Year (6 Semester) Multidisciplinary courses with Mathematics Minor under Curriculum & Credit Framework (CCF).
2. The CBCS-2018 System (Academic Session 2018-19 onwards): Three-Year (Honours & General) under CBCS-2018
Honours Syllabus General Syllabus
3. The 1+1+1 System, 2010 (Academic Session 2010-11 onwards): Three year B.Sc. (Honours & General) Courses in Mathematics, 2010.
Add-on courses conducted by the Department of Mathematics:
| Sl. No |
Year |
Topic |
| 1 | 2021-22 | Logical Tools & Techniques in Mathematics |
| 2 | 2022-23 | The Mathematica: Math solver, programmer and drawing tools |
| 3 | 2023-24 | Basic Statistics – A teaching aid in Mathematics |
Generally classes are taken in offline mode. Online classes are taken for the classes attended by the students of both the colleges, Sammilani Mahavidyalaya & K. K. Das College, under MOU. We frequently use smart classrooms, google classroom and powerpoint for better understanding of the students. Students are guided by the teachers to develop their knowledge on the basis of the following:
- Disciplinary Knowledge: Teaching plan & time schedule are used to prepare according to the Calcutta University Syllabus.
- Critical Reasoning & Problem Analysis: Faculties try to explain methodically all the nitty gritty of the theoretical portion of the syllabus with the help of related examples and problems.
- Development of Interdisciplinary Knowledge: There are topics such as Differential equations, Linear programming problem(LPP), Probability and Statistics, Discrete Mathematics, Statics and Dynamics enclosed in the syllabus, which have huge applications in different branches of science and technology, Commerce and also in the field of Arts. Special interdisciplinary lecture series also have been arranged for students of other departments for catering their needs. Recently, the department has offered an Interdisciplinary Course (Mathematics in daily life ) which has been included in the mathematics syllabus under NEP-2020, for students of other disciplines except Pure Science.
- Soft and technical Skill Development: In the mathematics syllabus under CBCS, 2018 and CCF, 2022, there are Skill Enhancement courses (SEC), like C-programming, SAGEMATH, PYTHON, LATEX softwares in which student used to undergo by the training of the departmental teachers to develop their communication.
- Self Directed learning: Learning by Student’s seminar method is regularly applied for 2nd and 3rd year students. Assignments are given to them by the teachers and they have to study and prepare a seminar lecture and present that in the class with an interactive session. Apart from this, advanced learners of final year are directed to study topics in the advanced field of mathematics and prepare a research survey project, under the guidance of departmental teachers.
- Experiential Learning: The Practical portion of the syllabus deals with soft and technical skill development of their study. They have to solve several mathematical problems by using C-programming language with the help of computers in the departmental computer laboratory under the guidance of teachers of the department.
- Employability options: Students used to learn Statistics, Discrete mathematics, Software like C programming, SAGEMATH, which are very helpful to participate in job fairs organized by the college for campus recruitment by various companies and also for any type of entrance examination and facing interviews.
- Develop research related skills: Advanced students are encouraged to do mini research projects. In the 2022-23 session, some students of the outgoing 6th semester prepared a survey report on Baudhayana – the Sulba-Sutras, guided by the faculty members Dr. Sumita Das and Ms. Sukti Sen of the Department of Mathematics.
Teaching Plan
Detail Teaching Plans are prepared before commencement of odd or even semesters. The links to the plans are given below.
Time Schedule: ODD Semester EVEN Semester
Teaching Plan: ODD Semester EVEN Semester
Mentor-Mentee
Remedial Classes
Remedial classes are taken after the Internal and Tutorial part of Calcutta University Examination. Remedial Class Schedule for 2023-24
Participative/ Experiential Learning
i) Experiential Learning
- Every year we arrange departmental seminars. Report on Departmental Seminar
- Also faculties guide students for preparing wall magazines, poster presentations etc. Poster & Wall Magazine
- We have conducted an educational tour on 11.10.2023 to Ramkrishna Mission Residential College. The faculties and Students attended a lecture by Dr. Parthasarathi Mukhopadhayay and visited “The ZERO GALLERY” there. Report on “ZERO Gallery Visit”
ii) Participative Learning:
- Celebrating National Mathematics Day – 2022, 2023 (Poster Presentation & Quiz) Event Report
- Student Seminars were organized regularly. Link to the details.
Question Bank Internal/ Tutorial University Question
Facilities
- Laboratory: There is a computer software laboratory associated with the department of Mathematics consisting of 20 computers for the usage of the students for the purpose of practical classes on Numerical methods, SEC classes like C-programming, SAGEMATH, Python and LATEX.
- Seminar Library: We have a formidable Departmental Library for reference books. Both teachers and students have access to this library. There is a departmental book issue register in which students and faculties register themselves for lending of books.
.
- ICT Facilities: In spite of the computer software laboratory, two Smart classrooms are frequently used for the students and faculties to take regular classes, seminar presentations, quiz contests etc. according to the requirements.
Evaluation System
The Internal and tutorial (Schedule) part of CU examinations for each semester and class tests are part of our regular evaluation system. In 1st semester there is a system to take an Entry level assessment test to evaluate their basic knowledge in Mathematics and distinguish advanced and slow learners.
Achievement of Students: Link to the details
Students Progression: Link to the details:
i) Experiential Learning:
- Every year we arrange departmental seminars.
- We have conducted an educational tour on 11.10.2023 to Ramkrishna Mission Residential College. The faculties and Students attended a lecture by Dr. Parthasarathi Mukhopadhayay and visited “The ZERO GALLERY” there.
ii) Participative Learning:
- Celebrating National Mathematics Day – 2022, 2023 (Poster Presentation & Quiz)
- Also faculties guide students for preparing wall magazines, poster presentations etc.
- Student Seminars were organized regularly.
- Student’s Project: Under the curriculum, students have to do small project works on each Major paper for the Tutorial part of the Calcutta University Examination. Students’ Project
- Mini Research Project(IKS): Students were encouraged to do mini research projects on Baudhayana – the Sulba-Sutras, guided by the faculty members Dr. Sumita Das and Ms. Sukti Sen of the Department of Mathematics. Mini Research Project
Co-curricular & Extra-curricular: The departmental students are very much involved in co-curricular and extra-curricular activities held in the college and outside.
Link to the details of the co-curricular and extra-curricular activities of the students are given below:
Sammilani Mahavidyalaya (SMV) has an Active Collaboration Agreement (MOU) with K. K. Das College (KKDC), Garia, a neighboring college, since 2020 under which faculties of Departments of Mathematics of both the colleges teach students of both SMV and KKDC. Both the colleges jointly organize various events like Departmental Seminar, National Mathematics Day etc.


Academic Session-wise Activity Under MOU:
Academic Session 2020-21 Academic Session 2021-22 Academic Session 2022-23 Academic Session 2023-24
Alumni Lecture Series:
| Session | Speaker | Batch | Schedule | Title of the Lecture |
| 2023-24 | Sri. Sukhdeb Naskar | 2018-21 | 16.02.2024 (12 noon to 2p.m.) | Fundamentals of Group Theory |
| 2024-25 | Sahir Ahmed Sardar | 2012-15 | 03.07.2024 (12 noon to 2p.m.) | An Overview of Vector Space |
Distinguished Alumni: Many of our students are associated with teaching and other professions. Some are pursuing higher studies. We wish them all the best.
| Sl. No. | Name | Batch | Present Status |
| 1 | Akash Gayen | 2017-19 | Inspector central GST & Central Excise |
| 2 | Sumana Chowdhury | 2018-21 | Sales Development Trainee |
| 3 | Kaushiki Ghosh | 2014-17 | Assistant Teacher in Mathematics of Happy Home English High School(H.S.), Batamore, Kolkata-700141 |
| 4 | Akash Mukherjee | 2016-18 | Document Verification Officer, Bandhan Bank |
| 5 | Bitangshu Kamila | 2009-12 | Krishna Chandrapur High School, South 24 Parganas |
| 6 | Debyani Manna | Ph.D. in IIT Roorki | |
| 7 | Dipankar Hazra | 2014 | Heramba Chandra College(SACT-I) |
| 8 | Sahir Ahmed Sardar | 2016 | Greater Kolkata College Of Engineering & Management |
Teachers’ Day & Reunion





Alumni Seminar





Educational Tour





